Walkthrough
If you're reading this, you probably already know at least a little about mQuark. Let's go over how we integrate mQuark, which seems to be complex but based on very simple logic, into our entity through examples.
First of all, to recap what mQuark is: mQuark is an NFT Protocol with extended capabilities and easy to use for all the people from all the backgrounds.If you would like to learn more, we strongly suggest you to visit our Glossary here.
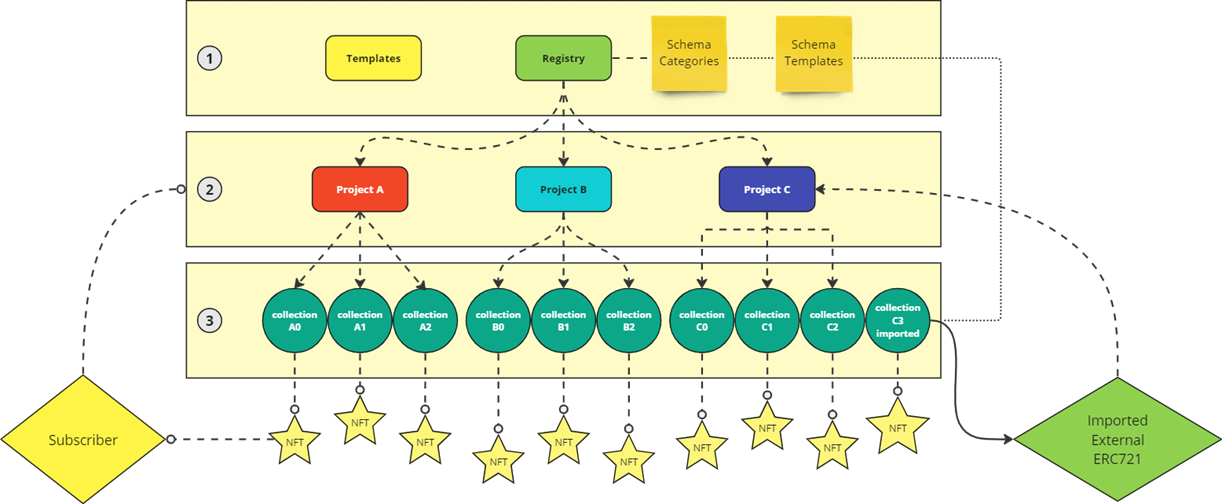
If we would explain mQuark logic, entities will register to the Protocol. They create collections from already prepared Template catalogs by the mQuark team; collections will be defined by another metadata that will ease the understanding of the meaning of NFTs.
To learn more about the collection creation process, you can visit the Create Collection section of the documentation.
You can also get more information about the Collection, please see here.
Template prices are set by mQuark Team.
After successfuly registering and creating collections, the next step is to be able to list your collections to be minted by end-users. To learn more about the minting process, you can visit the Mint NFT section of the documentation.
Users with their minted mQuark NFTs can subscribe to the mQuark Entities. Subscription creates another URI on the NFT, making the NFT multi-asset. Only the Entity that the NFT is subscribed to can update the NFT's metadata with the permission of the token owner.
If you've registered and created your collections and if you say "ok, what should I do now?", fasten your belts tight; here we go!.
Make Your own mQuark Store (NFT Mint Page)
Before we start, please remember that write functions that update the state of the smart contract, like mint, subscription etc, it is required to connect a wallet.
After creating the collections, the first thing to do is to list them on your website/entity/game so that end-users can mint them. If you were a baker, you would definitely put your cakes on your shelves to sell to your customers; that's what we do here as well!
Since everything happens through smart contracts, if the end-user has the necessary knowledge and experience, they can perform the mint on the smart contract. The listing we do here is to create the UI and make the mint process as easy and understandable to the user as possible.
In order to list the collections, we need to get some information from our end-points. We suggest you use this following information when listing your NFTs.
Mint
We use GraphQL APIs. If you need to know more about GrapQL logic, visit their docs.
- A collection you created consists of a number of NFTs ready to be minted by the end-users. It would be appropriate to show our collections' total supply and the number of left NFTs. To show them, we should add the
totalSupplyandmintedCountto our API query.(See Query 1.1)
A collection contains tokens that are not yet in existence, which is transferred to the blockchain after minting. If a collection's total supply is specified as 10.000 and the minted count is 0, there has not yet been a transfer from that collection to the chain. When it is started to be minted, the minted count will increase by the minted number and when it is equal to the total supply, the mint will no longer occur.
Thus, when listing a collection, users can see information such as "maximum total supply, and the number of available NFTs".
Mint Price
If a collection is paid, users need to send the correct amount to the contract. Collection prices can be queried by in this example query
Example Queries
Query a collection
query EntityCollection($_id: ID!) {
entityCollection(id: $_id) {
address
balance
collectionId
collectionURIs
controller
dynamic
free
id
mintLimit
mintPrice
mintType
mintedCount
entityId
protocolBalance
protocolWithdrawnAmount
royalty
templateId
totalSupply
totalWithdrawnAmount
verifier
whitelisted
witdrawnAmount
template {
id
uri
templateId
category
}
}
}
[Query 1.1]
You can see a sample query above [Query 1.1]. Here you can query the collections created by the entity.
Query a collection - Response
Here you can find the response.
{
"data": {
"entityCollection": {
"address": "0x19a4976bd3eed8350329e7aeb3b1cce5c688fb07",
"balance": "30000000000",
"collectionId": "1",
"collectionURIs": ["https://mquark.infura-ipfs.io/ipfs/QmXvgn4mjfdyENsRGw6KmQniW2TVBEVGMzztLyyPiNb7wC"],
"controller": "0x75d3bfa68c6990b0df9dbf80e4f9dc083456795a",
"dynamic": false,
"free": false,
"id": "0x19a4976bd3eed8350329e7aeb3b1cce5c688fb07",
"mintLimit": "5",
"mintPrice": "10000000000",
"mintType": 5,
"mintedCount": "3",
"entityId": "2",
"protocolBalance": "90000",
"protocolWithdrawnAmount": "0",
"royalty": "333333",
"templateId": "1",
"totalSupply": "10000000000",
"totalWithdrawnAmount": "0",
"verifier": "0xc52d3ecb7f84a27c68541933fdd5b74b96334c05",
"whitelisted": false,
"witdrawnAmount": "0",
"template": {
"id": "1",
"uri": "https://mquark.infura-ipfs.io/ipfs/QmbXSdoDAQtEPCx9aXv2spLnwQgq2wfZ4mLYyFzi7VdTGc",
"templateId": "1",
"category": "vehicle"
}
}
}
}
[Query 1.1 response]
Smart contract Functions
After listing collections, they should be minted properly. Related mint functions should be called in mQuark Control contract.Only free mint functions are called from mQuark directly. You can check our techical reference section here.
If the list will be on a web page, useful libraries like ethers.js or web3.js (we recommend ethers.js) can be used. For your unity-based entities, you can use this document prepared by ChainSafe team.
You will need our smart contract's addresses and ABIs. (TBA)
Getting User mQuarks in Wallet
The most important query for entities is reading end-users wallets. Wallets can be querid by the Graph API.
This gives an opportunity for developers to build their own logic with mQuarks. Since mQuark only provides standardization to the NFT ecosystem, it is totally up to the entity how to use them in their business.
To query users' mQuarks, here is a basic implementation.
query Owner($_id: ID!) {
owner(id: $_id) {
id
quarks {
id
tokenId
collectionId
contractAddress
entityId
templateId
immutableUri
isLocked
subscriptions {
id
asset
}
}
}
}
[Query 2.1]
Here you can see the response. You can also see that the user has 3 mQuarks and one has two subscriptions.
{
"data": {
"owner": {
"id": "0x2d323fbfdc22be7d8e3652cb4032c34ee2e3b667",
"quarks": [
{
"id": "0x19a4976bd3eed8350329e7aeb3b1cce5c688fb07-0",
"tokenId": "0",
"collectionId": "1",
"contractAddress": "0x19a4976bd3eed8350329e7aeb3b1cce5c688fb07",
"entityId": "2",
"templateId": "1",
"immutableUri": "https://mquark.infura-ipfs.io/ipfs/QmXvgn4mjfdyENsRGw6KmQniW2TVBEVGMzztLyyPiNb7wC",
"isLocked": false,
"subscriptions": [
{
"id": "2-0x19a4976bd3eed8350329e7aeb3b1cce5c688fb07-0",
"asset": "ipfs://QmXr1F9cSF3YXH2cTq2X8Pf3cyTFPtvjqhq7Qyqo6Axj9s"
}
]
},
{
"id": "0x19a4976bd3eed8350329e7aeb3b1cce5c688fb07-1",
"tokenId": "1",
"collectionId": "1",
"contractAddress": "0x19a4976bd3eed8350329e7aeb3b1cce5c688fb07",
"entityId": "2",
"templateId": "1",
"immutableUri": "https://mquark.infura-ipfs.io/ipfs/QmXvgn4mjfdyENsRGw6KmQniW2TVBEVGMzztLyyPiNb7wC",
"isLocked": false,
"subscriptions": [
{
"id": "1-0x19a4976bd3eed8350329e7aeb3b1cce5c688fb07-1",
"asset": "ipfs://QmXr1F9cSF3YXH2cTq2X8Pf3cyTFPtvjqhq7Qyqo6Axj9s"
},
{
"id": "2-0x19a4976bd3eed8350329e7aeb3b1cce5c688fb07-1",
"asset": "ipfs://QmXr1F9cSF3YXH2cTq2X8Pf3cyTFPtvjqhq7Qyqo6Axj9s"
}
]
},
{
"id": "0x753ef8763ebb89a479957fbd5c644db9b034cc09-3",
"tokenId": "3",
"collectionId": "1",
"contractAddress": "0x753ef8763ebb89a479957fbd5c644db9b034cc09",
"entityId": "1",
"templateId": "1",
"immutableUri": "https://mquark.infura-ipfs.io/ipfs/QmXvgn4mjfdyENsRGw6KmQniW2TVBEVGMzztLyyPiNb7wC",
"isLocked": false,
"subscriptions": []
},
{
"id": "0x753ef8763ebb89a479957fbd5c644db9b034cc09-4",
"tokenId": "4",
"collectionId": "1",
"contractAddress": "0x753ef8763ebb89a479957fbd5c644db9b034cc09",
"entityId": "1",
"templateId": "1",
"immutableUri": "https://mquark.infura-ipfs.io/ipfs/QmXvgn4mjfdyENsRGw6KmQniW2TVBEVGMzztLyyPiNb7wC",
"isLocked": false,
"subscriptions": []
}
]
}
}
}
[Query 2.1 response]
The NFT that has been not subscribed to your entity
- Entities will interact with their slots on NFTs. This slot will store the URI(asset) for your entity. Whatever is in there should represent something for your entity. So, if this slot is empty or there isn't one for your entity, that means the token the user has is a brand new NFT for you. And if this is the first time you have saved any information regarding this token ID in your database, also. Because it is also possible for you to handle the logic in a centralized way, centralization will prevent interoperability for NFT for your entity since other entities need to access the information on what attributes an NFT has. The only way for them to access the info is to read the slot on NFT that belongs to you.
To check an NFT's slot for your entity, use either a useful query or a smart contract function;
- #tokenEntityURI is the smart contract function which belongs to mQuark contract. With passing your entity and token ID to the function, it returns the URI.
As you can see on the response [Query 2.1 response] user's token ID: 2 NFT has two subscriptions to entity ID: 1 and entity ID: 2. However for the token ID: 3 or token ID: 4, there is not any open slot.
Some possible approaches in this stuations;
After you detect it is not subscribed to your entity with the NFT, you may ask the user whether they would like to subscribe;
- User wants to subscribe; subscribeToEntity function does the job for you. (There are also batch functions)After the user has been subscribed, the slot will be pre-filled with the default URI you provided during entity registration. If your entity is a game, and since you know the NFT's template ID, and the template ID refers to a type, e.g. vehicle, car, house etc., you may give the user a proper item and also you may add randomized attributes or customized ones by the user to the item(The logic here is totally up to you). The important thing you need to consider is that since the user opened the uri slot and when they get the respective item from you, the uri slot still doesn't have the respective item's metadata inside.tip
It is also possible for you to give your users an option to subscribe to other entities, as well. However, of course the money goes to the entity owner.
Since this is your uri slot and attributes, if the user updates the metadata, after you prepared the new URI, you may add also in-game item ID which is given to the user, as an attribute to the metadata. Every time you read the item ID, you may provide that item to that NFT owner.noteSince NFTs are tradable, checking users' NFTs every time they connect to the game is recommended.
- User wants to subscribe; subscribeToEntity function does the job for you. (There are also batch functions)
- After the user receives the item for the first time, they exit the game without updating the slot. The item ID is saved in-game with this NFT. The user logs back into the game. His wallet is rechecked and still has the same NFT. The user continues to use the item without the slot being read.
- After the user receives the item for the first time, they exit the game without updating the slot. The item ID is not saved in-game with this NFT. The user's wallet is checked and the slots are read again and the item matching the registered data in the slot is transferred to the user.
- After the user receives the item for the first time, he exits the game without updating the slot. The NFT is transferred to another user. User logs back into the game. In-game records of this user is compared with his blockchain wallet, and the in-game item is taken from the user as he no longer owns the transferred token(NFT). When the current owner of the transferred token enters the game, his blockchain wallet is checked, the NFT is found, and since the metadata exists for the entity, the item is given to the user according to the metadata. (If the same user continues to enter the game without transferring NFT, regardless of the item's properties in the metadata, The latest version can be given to the user.)
- User doesn't want to subscribe;
- If this is the case, keep the record of the NFT Token ID with the connected user address. Since the given item to the user is an in-game item, tracking the item should depend on the consistency of the user until having the NFT in his wallet or detecting the same NFT in another user's wallet. Item will be bound to the NFT. If the user continues to keep the NFT, the user's in-game item should be kept with its updates, but if the NFT owner changes, the item can be reset to its initial state and sent to the new NFT owner and removed from the former NFT owner.
- You may also accept other entities metadata. See the section below. You may read the other entity slots and ask users to choose among valid entities and you can transfer the selected metadata or interpret it to your entity.
As you can see, there are many approaches to how to use mQuark in your games/business. As NFT represents ownership and since you are the owner of the game you decide how to play with it.
Updating URI requires a transcation fee from the user. So, users may be reluctant to pay the fee so as a result they would like to update their metadata rarely. This should be kept in mind.
For furher detailed querie please check our API documentation here.
So far, we have seen why do we need to make a marketplace, what information are needed to make one, example queries, reading users NFTs in their wallets and possible cases for NFTs. If you have any further questions or wonder about something else, please don't hesitate to contact us via approval@soonami.io.
Updating the Metadata
Updating the Metadata of an NFT requires you to validate the update and sign the signature with your registered address.You should create a new metadata and then you may upload it to your own cloud or we can handle the upload and return the URI(in progress). After that, you prepare the transaction for the user to send it to the smart contract. Here is the smart contract function.
If you would like to learn how to sign a data with blockchain wallets, ethers.js is an usefull library. A YouTube tutorial can be helpful.
Reading Details of Other Metaverses/Entities
Since mQuark's purpose is to be an interoperable NFT entity, it is important to view other registered entities useful information like ID, wallet address etc. These information will be required when you would like to access an mQuark NTF's metadata for other entities. So, you may accept/reject the metadata coming from other worlds. Since you are the owner of the game, this is totally up to you how you use those metadata in your games/entities.
Here is an example Query and its response;
query Entites {
mquarkEntities {
name
owner
entityId
description
defaultURI
contractAddress
subscriptionPrice
}
}
{
"data": {
"mquarkEntities": [
{
"name": "My Favourite MMORPG",
"owner": "0xfe7bc9d3dfd961226b621fc9b10be7acecaf497f",
"entityId": "1",
"description": "The best MMORPG ever!. It's all about PVP, PVE and trade! Come and join!",
"defaultURI": "ipfs://QmXr1F9cSF3YXH2cTq2X8Pf3cyTFPtvjqhq7Qyqo6Axj9s",
"contractAddress": "0xef708cb1008ef7357602895393a5709eb94c1783",
"subscriptionPrice": "10000000000000"
},
{
"name": "My Car Store",
"owner": "0x2d323fbfdc22be7d8e3652cb4032c34ee2e3b667",
"entityId": "2",
"description": "The best cars in the world are here! Check the newest NFTs!",
"defaultURI": "ipfs://QmXr1F9cSF3YXH2cTq2X8Pf3cyTFPtvjqhq7Qyqo6Axj9s",
"contractAddress": "0xed38054d92bb58e525aa380c133d73e58f2d4455",
"subscriptionPrice": "100000000000000"
}
]
}
}
Reading Their Metadata
Here is the smart contract function that allows you to read other metaverses/entities metadata.
Binding Current Item/Asset to mQuark
Users may would like to bind their in-game assets or even an achievement or a character to a NFT. Why they would like to do this is explained also in our Whitepaper in Section 3. To be able to do that they need an NFT with an open uri slot for your entity.
Metadata makes it possible to bind an Item wit NFT. Item/asset ID in the game can be assigned to your metadata and it can be accessible by reading the metadata. You will have an option to transfer that item with that ID, to whoever owns this NFT which contains that item/asset ID in its metadata.